one-time new patient offer
$170
(includes comprehensive check up and clean, 3 sets of radiographs and fluoride treatment)
Need Dental Services?
Schedule Appointment
McDonald’s Road, South Morang VIC 3752
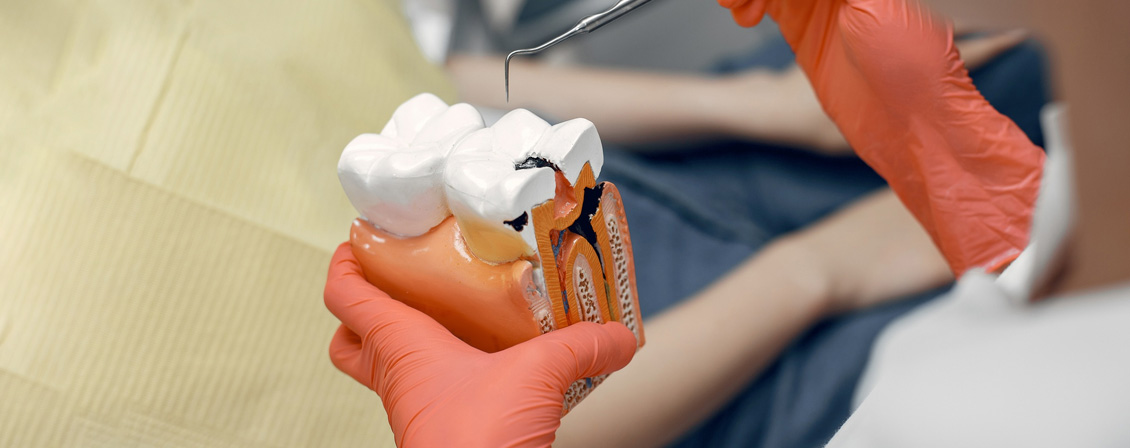
Why Do I Have Dental Caries? Understanding the Culprits Behind Tooth Decay Introduction
Home » Why Do I Have Dental Caries? Understanding the Culprits Behind Tooth Decay Introduction